Compression stockings enhance blood flow in the legs and prevent fluid accumulation for people who work long hours on their feet, travel regularly, or often work out. However, not everyone should wear compression socks. Some might have issues like itchiness, skin discomfort, or other conditions like peripheral neuropathy or peripheral artery disease. In this article, we will explore who should not wear compression socks and discuss their potential side effects. This will help you make better choices and informed decisions.
Medical-grade compression socks apply certain pressures that can be dangerous when worn inappropriately or without professional intervention. Patients with severe arterial disease, untreated congestive heart failure, or skin infections should not use them. Complications include worsening pain, tingling sensation, and skin breakdown if the sock is tight or used for a long time.
It is always advisable to seek medical advice before engaging in compression therapy. Proper guidance enables wearers to maximize the benefits of using socks while minimizing the risks associated with them.

Understanding Compression Therapy
Compression therapy involves wearing special clothing that exerts gentle pressure on the limbs, particularly on the legs. This assists in increasing blood circulation and minimizing inflammation, among other functions.
How Compression Socks Work
Compression stockings help by applying gentle pressure to the legs to encourage proper blood flow. They are typically tightest at the ankle and gradually loosen at the leg part. This design assists in reversing blood flow back toward the heart to avoid stagnation within the lower limbs. This can be particularly helpful for those who work standing or sitting most of the time. It helps lower inflammation and the chances of blood clots.
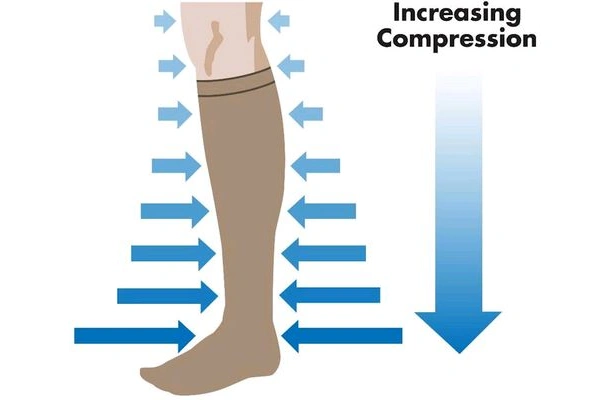
Source: https://www.pebbleuk.com/article/130/do-compression-socks-work/
Different Types of Compression Garments
Compression garments come in various categories, each serving specific functions. Compression stockings and socks are the most popular for everyday use. Graduated compression socks have varying levels of compression, with the highest pressure on the ankle. While compression sleeves are tight coverings that can be pulled up only as far as the knees or elbows, compression bandages are used for more localized pressure. The choice of compression garments depends on medical requirements and personal comfort preferences.
Finding the Correct Compression Level
Determining the right compression level is important in optimizing and wearing comfort. Pressure differentials are expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Moderate pressure range (8 to 15 mmHg) is suitable for daily wear. Light to moderate compression (15-20 mmHg) is used for mild swelling and varicose veins. Moderate to severe swelling and prevention of blood clot formation require firm compression (20-30 mmHg). Additional firm compression (30-40 mmHg) is required if one has serious issues with veins. However, it is advisable to seek the advice of a healthcare practitioner to get the right dosage for a specific user. Wearing the right size and using the product as intended helps optimize the advantages and reduce any potential harm.

Medical Conditions and Compression Socks
There are numerous medical conditions for which people wear compression stockings, and they can be advantageous and disadvantageous.
Potential Benefits for Venous Disorders
People with venous disorders are usually advised to wear compression socks. These socks enhance blood circulation, alleviating problems such as swelling and leg pain.
In particular, patients suffering from deep vein thrombosis or chronic venous insufficiency need to wear such stockings because they prevent blood clots in the legs. They are also used to treat varicose veins and help relieve the pain caused by this condition. Better circulation can also assist in treating ulcers resulting from chronic venous problems.
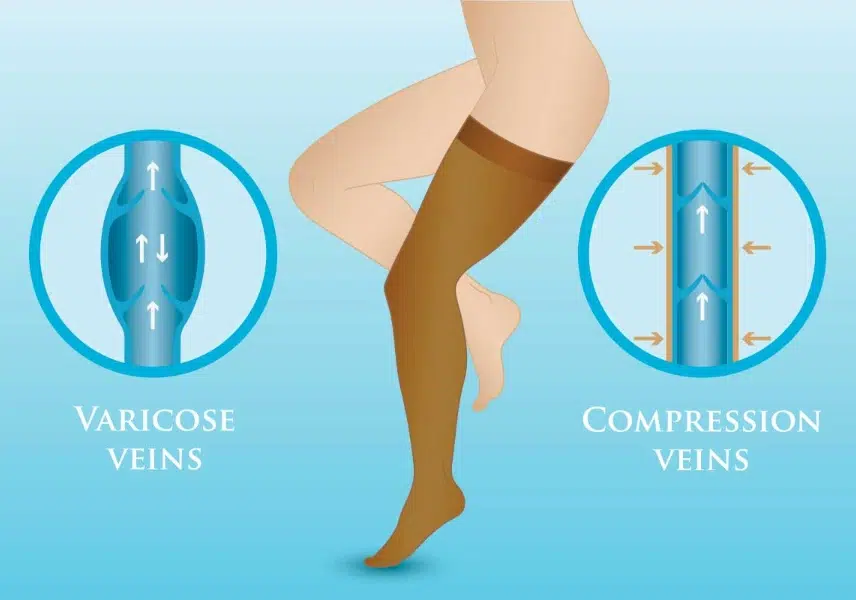
source: https://www.miamivein.com/compression-stockings-for-varicose-veins/
Risks Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease
Although compression socks are helpful for patients with venous disorders, they can be dangerous for peripheral arterial disease (PAD) patients. These socks apply pressure to the legs, potentially limiting blood circulation in patients with severe arterial conditions.
Some of the symptoms of PAD include pain and cramps in the legs, and these may become worse due to reduced blood flow. People with PAD or those who have peripheral neuropathy beyond the first degree should seek medical advice before using compression socks.
Conditions That Preclude the Use of Compression Socks
In some situations, wearing compression socks should be avoided. Uncontrolled congestive heart failure is one such condition because compression can make fluid build up and worsen heart symptoms.
Likewise, patients without proper treatment for septic phlebitis should not wear compression socks, as this may spread the infection further. Compression socks are contraindicated in peripheral artery diseases, where the arteries are mostly blocked. Please always seek the advice of a healthcare provider if compression therapy is suitable for your health condition.
Selecting the Right Compression Socks
To choose the right compression socks, one must consider the level of compression, the material used, and the fit. Proper selection improves comfort and provides added benefits such as better circulation.

Considering Compression Levels and Material
Pressure commonly varies from slightly high to very high. Mild compression (8-15 mmHg) is ideal for individuals experiencing mild swelling and fatigue. Medium compression (15-20 mmHg) is worn for moderate swelling and leg pain. Elevation (20-30 mmHg) is usually preferred for serious swelling and varicose veins cases.
Graduated compression stockings exert the highest pressure on the ankle and gradually reduce pressure toward the thigh. They are made of nylon, spandex, and Lycra fabrics, which make them elastic and long-lasting. Flexible materials are used to avoid skin rash and excessive sweating. It is always advised to seek medical advice when deciding on the right compression level and suitable material.
Tips for Proper Use and Fit
It is critical to get the right size for the best outcomes. Take the ankle, calf, and thigh girth measurements in the morning when swelling is likely at its lowest. According to the size chart given by the manufacturer, one should choose the correct size.
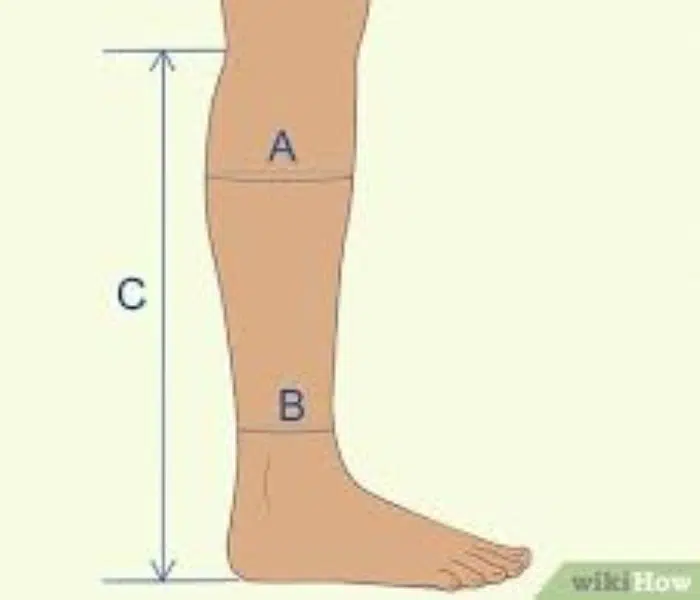
Source: https://www.wikihow.life/Measure-for-Compression-Socks
There are several pitfalls that patients should be cautious of when putting on their compression stockings, and they include: To put on socks, starting from the top, roll the sock down to the heel area, then put your foot into the toe of the sock and then roll up the leg gently. Tighten the sock to increase the amount of pressure applied evenly. They should be worn every day, but in the absence of special medical advice, it is best to take them off at night.
When to Replace Compression Socks
Compression socks should be replaced every three to six months for optimum results. Gradually, the elastic fibers may break down, resulting in the sock losing its elasticity or compression capacity. Indications that it’s time to buy a new pair include declining tightness, obvious slippage, and observable signs of tear and wear.
By monitoring your socks for these changes, you can prevent compromised performance. It is advisable to own a couple and use them in turns to ensure they last longer. Proper care, including washing hands before handling the stockings and air-drying, can also help increase the longevity of the compression stockings.
Following the above guidelines, users can take proper care of their legs and get the most out of compression stockings.
Potential Side Effects of Compression Socks
There are numerous benefits associated with wearing compression socks; however, several negative impacts may arise from their use or improper fitting. These issues relate to skin, circulation, and comfort.

Source: https://ahernspharmacy.com/pages/compression-socks
Identifying Improper Use and Fit Issues
Compression socks have to be worn properly so that they can work correctly. That is why when compression socks do not fit properly, they tend to fold and put pressure on certain areas, causing swelling and sore legs and feet. If socks are too tight, then a dangerous tourniquet effect occurs, which worsens conditions like varicose veins or blood clots. It is, therefore, important to ensure proper sizing and adherence to the recommended wearing periods to prevent such complications.
Skin-Related Complications
Some patients have complained of skin irritation, especially when using the material and tightness of the compression socks. This may be in the form of redness, itching, or, in the extreme, blister formation. Wearing improper socks for years could result in skin alteration, including making skin hard or thick. To reduce these issues, one should moisturize the legs and wear hypoallergenic socks. It is recommended that the skin under the socks be checked frequently, especially if one has sensitive skin.
Circulation Problems from Incorrect Usage
Failure to use the compression socks appropriately will result in poor blood circulation. If the socks are tight or not put on properly, they may narrow the blood vessels, which is not helpful in conditions such as deep vein thrombosis. It is important to make sure that these socks will put the right amount of pressure on the legs without being uncomfortable. Such problems are worsened if one wears them for long or during sleep without the doctor’s approval. Careful supervision of leg condition and regular changes in this case are required to maintain blood circulation.
Maintaining Healthy Legs with Compression Socks
Compression socks enhance blood flow, relieve inflammation, and regulate bodily fluids. However, to reap these benefits and mitigate the risks, one must follow best practices.

Photo by @ fotoblend (Pixabay)
Incorporating Compression into Daily Life
Wearing compression socks daily can help increase blood flow, as they exert slight pressure on the legs. This pressure also assists in avoiding the formation of clots and minimizes swelling. They should be put on as early as possible in the morning to be effective when the swelling has not taken place.
For optimal results, raise your legs at different times of the day. This helps drain fluids and reduces pressure on the calf muscles. It is advisable to remove the socks before going to sleep because when the body is in a horizontal position, blood circulation is facilitated.
Managing Fluid Accumulation and Swelling
Filled with special yarns, compression socks exert gentle pressure on the legs to facilitate the flow of lymphatic fluid. This is known as graduated compression, and the pressure applied is highest at the ankle and gradually decreases as it goes up the leg.
This compression assists the lymphatic system in pumping the fluid from the tissues back into the bloodstream. Regular use can enhance circulation and alleviate pain for those with venous disorders or leg ulcers. This technique does not require much effort but ensures proper blood circulation in the legs.

Source: https://www.lassogear.uk/blogs/news/wear-compression-socks-for-better-blood-circulation
Best Practices for Cleaning and Maintenance
Proper care of compression socks helps maintain their efficacy. It’s better to be washed after each use to retain their elasticity and enhance their cleanliness. Also, you can wash compression socks after wearing two days if you want, but not more than this period. If the fabric’s durability is to be maintained, using mild soap and water at a lukewarm temperature is advised.
Do not twist or wring the socks; roll them in a towel to remove as much water as possible, then spread them out to dry. Routine inspections are crucial to determine whether the garments are still in good enough condition to provide sufficient compression. Replacing them every few months or when they become less elastic is also advisable.

Source: https://www.ameswalker.com/blogs/news/wear-with-care-three-ways-to-keep-your-compression-socks-as-good-as-new
Conclusion
Compression socks offer various advantages, including enhanced blood circulation and prevention of swelling. They are relatively harmless for most consumers. However, some people should be careful. It is important to note that people with severe arterial diseases or severe peripheral neuropathy should avoid using them. Incorrectly fitting socks can lead to discomfort, skin redness, or even worsening of the condition.
One should seek the advice of a doctor before using compression socks, especially if one has other medical conditions. Complying with doctors’ recommendations when using compression stockings is mandatory to avoid adverse consequences. These are some of the actions that individuals can take to enhance the benefits with few side effects.
FAQs about Who Should Not Wear Compression Socks
1. How long should I wear compression stockings each day?
The duration of wearing compression socks may also differ based on the unique circumstances and medical situation. Usually, compression stockings should be worn during the day and taken off at night. Wearing them in the early morning is helpful to reduce swelling of the legs.
2. Can wearing compression stockings help with swollen legs?
Compression stockings help reduce leg swelling to a great extent. Through graduated pressure, blood and fluids are forced back up to the heart level to address issues concerning swollen legs.
3. Are compression stockings beneficial for improving leg veins health?
Leg veins greatly benefit from compression stockings. They aid in blood circulation, prevent the formation of varicose veins, and stop blood accumulation in veins. Compression stockings can be particularly useful for individuals with chronic venous insufficiency or for people who are on their feet for most of the day.
4. How do I choose the right compression stocking for my needs?
Choosing the right compression stocking involves considering the level of compression needed, which is measured in mmHg. Mild compression (8-15 mmHg) suits everyday wear and mild swelling. Moderate to firm compression (15-30 mmHg) is recommended for more significant issues like varicose veins and severe swelling. Consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate level and ensure a proper fit to maximize benefits and comfort.